We, as a group, study the photocatalyst/(co-catalyst)/water interface and aim for rational design of efficient and stable photocatalytic systems.
Photocatalytic water-splitting involves light absorption, generation of electron–hole pairs, charge separation and bulk transport, charge transfer across interfaces for catalytic reactions, and mass transfer of reactants and products.
In our latest study, we elucidated the charge transfer process at photocatalyst/(co-catalyst)/water interface and established a kinetic model. The Figure below shows the charge-transfer process at SrTiO3/Pt/water junctions (Pt co-catalysts not shown in the badn diagram for clear illustration), and steady-state current-potential behavior of SrTiO3 photoelectrodes in the dark and under illumination.
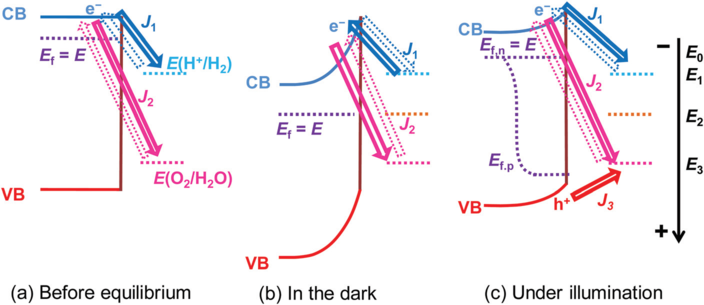
In short, our work revealed that the energetics of photocatalysts during operation was correlated with the kinetics of the charge transfer process and the kinetic-controlled energetics affect charge separation efficiency sensitively.